Cisco Packet Tracer (CPT) Lab Solutions - Configure Initial Router Settings.
Easy steps to configure a router's initial settings using the cisco packet tracer
Overview
This Cisco Packet Tracer lab is a property of the Cisco Networking Academy, Skills for all with Cisco. This article seeks to bring solutions by displaying images and providing answers to the questions in the lab for better understanding.
Click the Cisco Packet tracer file to get the lab file to follow up with the solution.
Objectives
Part 1: Verify the Default Router Configuration
Part 2: Configure and Verify the Initial Router Configuration
Part 3: Save the Running Configuration File
Background
In this activity, you will perform basic router configuration tasks. You will secure access to the CLI (Command Line Interface) and console port using encrypted and plain-text passwords. You will also configure messages for users who are logging into the router. These banners warn unauthorized users that access is prohibited. Finally, you will verify and save your running configuration.
Instructions
Part 1: Verify the Default Router Configuration
Step 1: Establish a console connection to R1.
a. Choose a Console cable from the available connections.
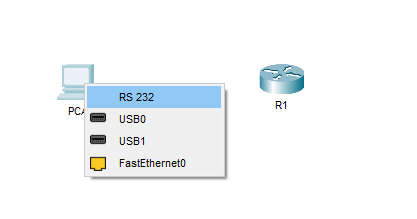
b. Click PCA and select RS 232
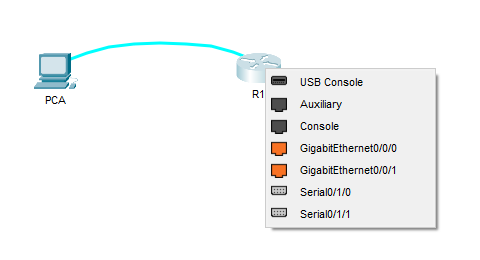
c. Click R1 and select Console
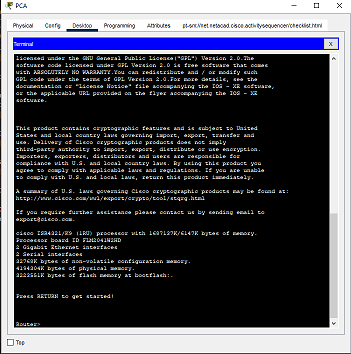
d. Click PCA > Desktop tab > Terminal
e. Click OK and press ENTER. You are now able to configure R1.
Step 2: Enter privileged mode and examine the current configuration
You can access all the router commands from privileged EXEC mode. However, because many of the privileged commands configure operating parameters, privileged access should be password-protected to prevent unauthorized use.
a. Enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the enable command
1
2
Router> enable
Router#
Notice the prompt changed in the configuration to reflect privileged EXEC mode.
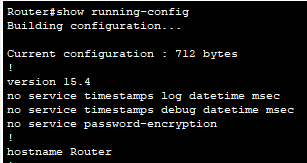
b. Enter the show running-config config
Question 1:
What is the router’s hostname?
Click here for answer
Router.Question 2:
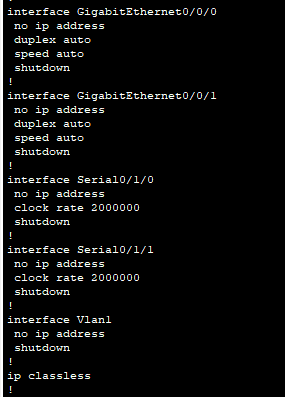
How many Fast Ethernet interfaces does the Router have?
Click here for answer
none.Question 3:
How many Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does the Router have?
Click here for answer
2.Question 4:
How many Serial interfaces does the router have?
Click here for answer
2.Question 5:
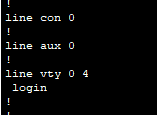
What is the range of values shown for the vty lines?
Click here for answer
The range is 0 - 4.c. Display the current contents of NVRAM.
1
2
Router# show startup-config
startup-config is not present
Question 6:
Why does the router respond with the startup-config is not present message?
Click here for answer
It displays this message because the configuration file was not saved to the NVRAM. Currently, it is only located in the RAM.Part 2: Configure and Verify the Initial Router Configuration
To configure parameters on a router, you may be required to move between various configuration modes. Notice how the prompt changes as you navigate through the IOS configuration modes.
Step 1: Configure the initial settings on R1.
The following tasks should be completed when configuring initial settings on a router.
Configure the device name using the name hostname1.
1
Router(config)# hostname hostname1
Secure privileged EXEC mode using password1 as the password.
1
Router(config)# enable secret password1
Secure user EXEC mode.
1 2 3
Router(config)# line console 0 Router(config-line)# password password1 Router(config-line)# login
Secure remote Telnet / SSH access.
1 2 3
Router(config)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# password password1 Router(config-line)# login
Secure all passwords in the config file.
1 2
Router(config-line)# exit Router(config)# service password-encryption
Provide legal notification.
1
Router(config)# banner motd delimiter message delimiter
The legal notification warns users that the device should only be accessed by permitted users. Legal notification as an example is configured as follows :
1 2 3 4 5 6
R1(config)# banner motd # Enter TEXT message. End with the character '#'. *********************************************** WARNING: Unauthorized access is prohibited! *********************************************** R1(config)#
Save the configuration.
1
Router# copy running-config startup-config
Open a configuration window, to continue the task
a. Configure R1 as the hostname.
b. Configure Message of the day text: Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited.
c. Encrypt all plain text passwords.
Use the following passwords:
Privileged EXEC, encrypted: itsasecret
Console: letmein
Step 2: Verify the initial settings on R1.
a. Verify the initial settings by viewing the configuration for R1.
Question 7:
What command do you use?
Click here for answer
show running-config.b. Exit the current console session until you see the following message:
1
2
3
R1 con0 is now available
Press RETURN to get started.
c. Press ENTER; you should see the following message:
1
2
3
4
5
Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited.
User Access Verification
Password:
Question 8:
Why should every router have a message-of-the-day (MOTD) banner?
Click here for answer
Every router should have a banner to warn unauthorized users that access is prohibited. MOTD Banners can also be used to send messages to network personnel(such as impending system shutdowns or who to contact for access).Question 9:
If you are not prompted for a password before reaching the user EXEC prompt, what console line command did you forget to configure?
Click here for answer
R1(config-line)#login.d. Enter the passwords necessary to return to privileged EXEC mode.
Question 10:
If you configure any more passwords on the router, are they displayed in the configuration file as plain text or in encrypted form? Explain.
Click here for answer
The service password-encryption command encypts all current and future passwords.Part 3: Save the Running Configuration File
Step 1: Save the configuration file to NVRAM.
Open a configuration window
a. You have configured the initial settings for R1. Now back up the running configuration file to NVRAM to ensure that the changes made are not lost if the system is rebooted or loses power.
Question 11:
What command did you enter to save the configuration to NVRAM?
Click here for answer
copy running-config startup-config.Question 12:
What is the shortest, unambiguous version of this command?
Click here for answer
cop r st or copy run start.Question 13:
Which command displays the contents of the NVRAM?
Click here for answer
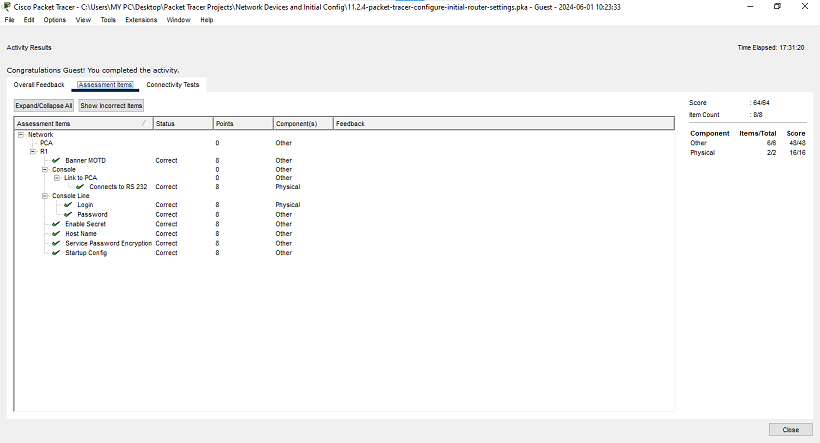
show startup-configuration or show startb. Verify that all the parameters configured are recorded. If not, analyze the output and determine which commands were not executed or were entered incorrectly. You can also click Check Results in the instruction window.
Step 2: Optional: Save the startup configuration file to flash.
Although you will be learning more about managing the flash storage in a router in later chapters, you may be interested to know that, as an added backup procedure, you can save your startup configuration file to flash. By default, the router still loads the startup configuration from NVRAM, but if NVRAM becomes corrupt, you can restore the startup configuration by copying it over from flash.
Complete the following steps to save the startup configuration to flash.
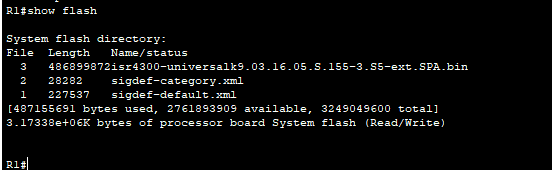
a. Examine the contents of flash using the show flash command:
1
R1# show flash
Question 14:
How many files are currently stored in flash?
Click here for answer
3.Question 15:
Which of these files would you guess is the IOS image?
Click here for answer
isr4300-universalk9.03.16.05.S.155-3.S5-ext.SPA.binQuestion 16:
Why do you think this file is the IOS image?
Click here for answer
Answers may vary, but two clues are, the file length compared to the others and the .bin at the end of the file name.Question 17:
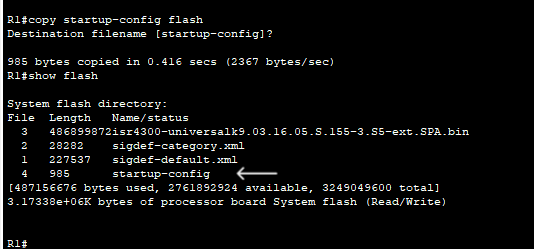
b. Save the startup configuration file to flash using the following commands:
1
2
3
R1# copy startup-config flash
Destination filename [startup-config]
The router prompts you to store the file in flash using the name in brackets. If the answer is yes, then press ENTER; if not, type an appropriate name and press ENTER.
c. Use the show flash command to verify the startup configuration file is now stored in flash.
Close the configuration window